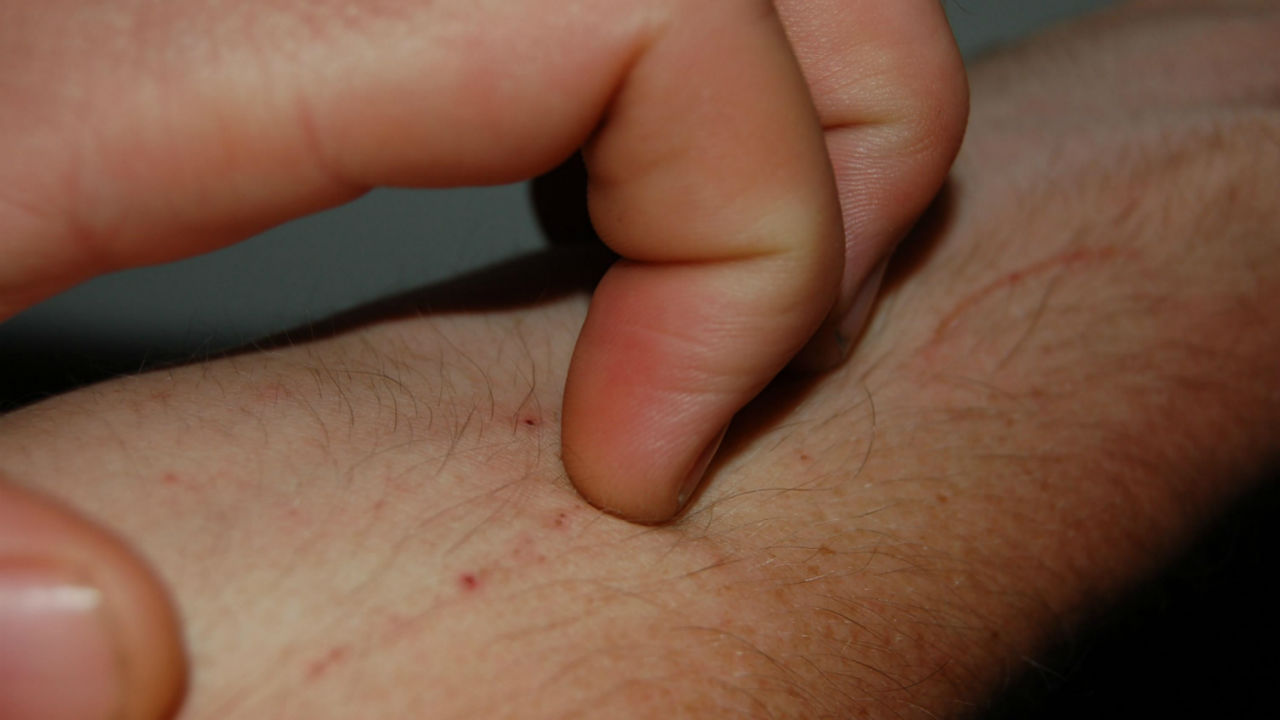
Ever have a spot that severely itches or see someone constantly scratching a thickened patch of skin? Neurodermatitis is form of eczema or atopic dermatitis where nerve endings in the skin become overly irritated leading to a cycle of excessive scratching and itching. Red patches appear on the skin covered with white scratch lines from the person’s attempts to relieve the intense itching.
Neurodermatis, also called lichen simplex chronicus, typically starts as a roughened patch on the wrist, neck, forearm, thigh or ankle. Excessive scratched causes the area to develop sore red spots and the skin can become overly thickened. Neurodermatitis can also affect the genital area involving the vulva or scrotum. Diagnosis of neurodermatis can be made through a skin patch test to determine if there is some type contact allergy causing the intense itching or by a skin biopsy to rule out a skin infection.
Who is at risk?
People who already have allergies, or other skin conditions such as psoriasis or other forms of dermatitis are more susceptible to neurodermatitis. Women, especially those between the ages of 30 to 50, are more likely to develop it.
In addition, certain circumstances or exposures to skin irritants can make someone more at risk for developing neurodermatitis. Tight clothing, dry skin, exposure to excess heat, insect bites or increased emotional stress may contribute. People have developed neurodermatitis after exposure to hair dye with the additive P-phenylenediamine (PPD), which has been found to cause allergies in some. See my article "Allergic to Hair Dye?" at www.empowher.com/allergic-contact-dermatitis/content/allergic-hair-dye
Treatment:
Treatment for neurodermatitis centers on the use of topical creams. Topical steroids reduce inflammation and topical keratolytics help reduce the thickening of the skin. Oral or topical antibiotics may be given to prevent infection from the excessive scratching. Antihistamines, both oral and topical, can reduce itching and a prescription sedative medication may help improve sleep at night.
Other alternative treatments are also an option. Placing cloths dipped in witch hazel or spreading camphor ointment may soothe irritated areas. Hypnosis may be successful in retraining the mind to ignore the itch.
If you develop neurodermatitis, it is important to avoid situations that allow the skin to become over irritated from scratching. Keep the itching area covered with clothing or a bandage, especially at night to prevent scratching during sleep. Try taking a cool bath, with or without oatmeal preparations such as Aveeno. Keep your fingernails short and filed smooth. Lastly, try to reduce stress and anxiety, which may trigger more of a desire to scratch.
sources:
www.mayoclinic.com/health/neurodermatitis/DS00712
www.skincarephysicians.com/eczemanet/neurodermatitis.html
Michele is an R.N. freelance writer with a special interest in woman’s healthcare and quality of care issues. Other articles by Michele are at www.helium.com/users/487540/show_articles



Add a CommentComments
There are no comments yet. Be the first one and get the conversation started!