 Photo: Getty Images
Photo: Getty Images
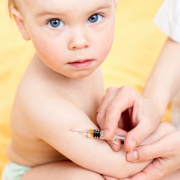
When my children were small and due for their shots, the doctor's office advised giving them acetaminophen drops before getting a vaccination. Some years before that the usual routine was to give a child some baby aspirin before shots but Reye's syndrome put a sudden stop to that practice.
According to some research from the University of Defence in Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic, it would appear that acetaminophen used to reduce any fever from a vaccination should go the way of baby aspirin.
Research reported in the October 17, 2009 edition of The Lancet that children aged 3 to 5 months who had been given acetaminophen before some immunizations had decreased immune response. The vaccines reported were for diphtheria, haemophilus influenza type B (Hib), pertussis, pneumococcal disease and tetanus.
Diphtheria is a bacterial infection that affects the nose and throat. Early symptoms are fever and swollen glands in the neck. Continuing infection can cause double vision, slurred speech and problems in breathing or swallowing,
Haemophilus influenza type B (Hib) can cause bacteremia, pneumonia and acute bacterial meningitis in children. It can also cause cellulitis, epiglottitis, infectious arthritis and osteomyelitis.
Pertussis is also known as whooping cough and affects the respiratory system. In children, pertussis usually starts with a cough, fever and runny nose.
Pneumococcal disease is caused by bacteria that can invade the lungs, the bloodstream, and the brain.
Tetanus, also called lockjaw, is caused by a bacteria that enters the body through a wound. Painful muscle spasms lead to problems such as drooling, problems with swallowing and opening the mouth.
Children aged 12 to 15 months, who had acetaminophen after booster shots for Hib, pneumococcal disease and tetanus still had diminished immune responses.
A Eurekalert! public release from December 1, 2009 referred to research from the University of Missouri indicating that aspirin and acetaminophen have an inhibiting effect on enzymes which then render some vaccines less effective.
Aspirin and acetaminophen seem to deter the enzyme COX-1 from doing its job in body tissues. This in turn can reduce the level of antibodies produced, which can weaken the immune system's defenses.
An additional finding was that regulation of inflammation -- which is the reason people take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs -- is a mixed blessing. These types of drugs don't just reduce pain and inflammation. They also reduce the body's antibody response which lessens our defenses against infection.
In an editorial accompanying the 2009 research from the Czech Republic, Dr. Robert Chen of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has indicated that the use of fever-reducing drugs needs to be re-evaluated in regards to immunization.
Resources:
Post-Vaccine Tylenol May Harm Immune Response
http://abcnews.go.com/Health/SwineFlu/tylenol-shots-hurt-vaccines-effectiveness/story?id=8840239
Aspirin, tylenol may decrease effectiveness of vaccines
http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2009-12/uom-atm120109.php
Visit Jody's website and blog at http://www.ncubator.ca and http://ncubator.ca/blogger
Reviewed June 15, 2011
Edited by Alison Stanton




Add a Comment2 Comments
Acetaminophen after MMR has also been linked to autism, see study here:
http://aut.sagepub.com/content/12/3/293
It also masks side-effects that the child may experience, and if any of these are serious it could delay appropriate medical attention.
It is also another drug to add to the drugs the child has just been injected with and vaccines also contain antibiotics so that is another drug. As a parent, I would certainly be concerned about the strain on the liver, particularly as there are frequent vaccinations throughout the child's first 18 months and if I had chosen to vaccinate I would have used breast milk instead, see this study on reducing vaccine pain with breast milk:
http://www.npjournal.org/article/S1555-4155(09)00578-9/abstract
And this one says breast fed babies have less vaccine side-effects than bottle fed ones:
http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/125/6/e1448.full.pdf
June 17, 2011 - 8:27amThis Comment
Acetaminophen presents other dangers besides possibly reducing the effectiveness of vaccines. Giving an infant too much of the drug could cause an accidental overdose resulting in liver failure - http://www.liverfailurefromtylenol.com/ - or even death. Always read the directions on all medications to avoid such a tragedy. Regards, TM
June 16, 2011 - 9:07amThis Comment