The skin cancer melanoma is colorblind. This non-discriminating cancer affects Latinos and African-Americans as well as Caucasians. According to the American Cancer Society, men have a higher incidence of melanoma compared to women and Caucasians have a 10 times greater risk of developing melanoma than African-Americans.
There is also a host of other risk factor for melanoma. Those include:
• Over-exposure to the sun’s rays
• Family history of the disease
• High incidence of sunburn
• Skin moles
• Age
• Past incident of melanoma
• Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP)
• Compromised immune system
The exact cause of melanoma is unknown. However, many medical experts believe ultra violet (UV) rays from a tanning booth or the sun can alter your DNA.
Also, some skin moles may turn into melanoma. It is a mystery why the DNA of some moles transform into melanoma while others do not. Melanoma may begin with a skin mole or appear on our skin without warning.
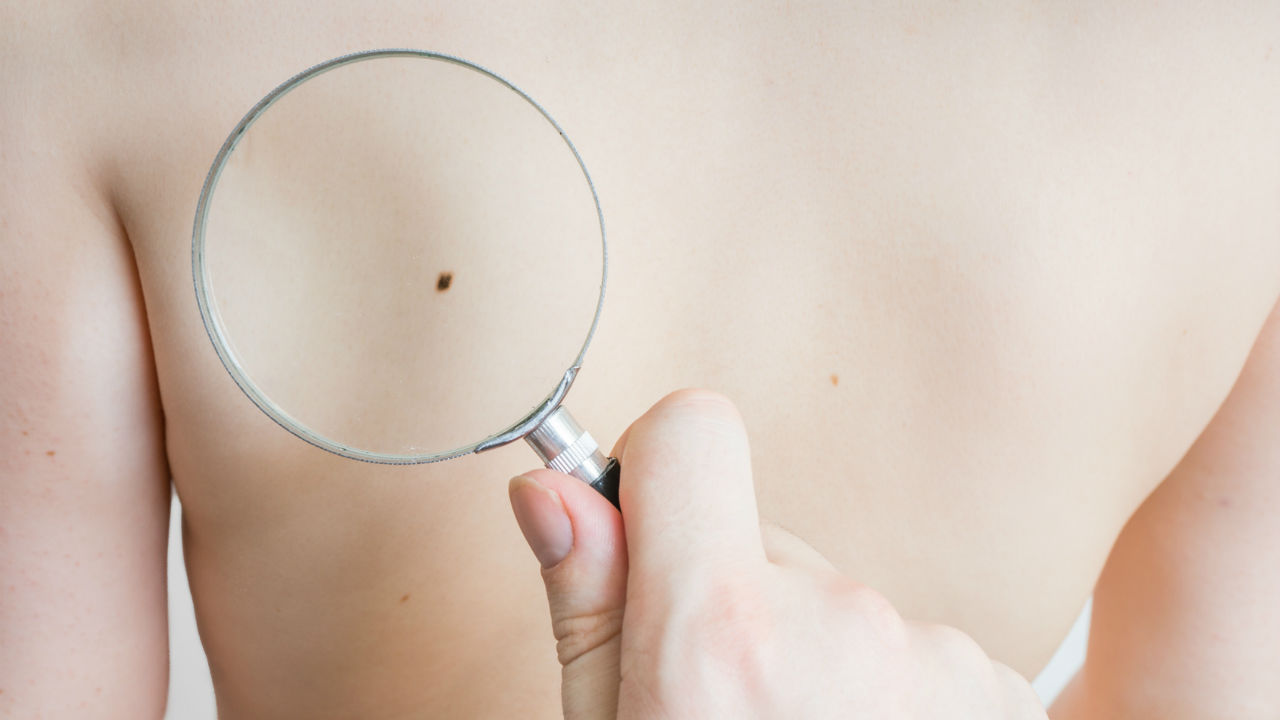
It is vital to your skin health to observe and watch your skin moles. The most important warning sign is a change in your mole or new skin growth.
Skin moles come in all shapes, sizes and colors. Some are raised off the skin while others lay flat and seem to blend into the skin.
The majority of our moles are harmless and look like chocolate spots on our bodies.
However, the American Cancer Society recommends the following ABCD rule when checking a suspicious mole:
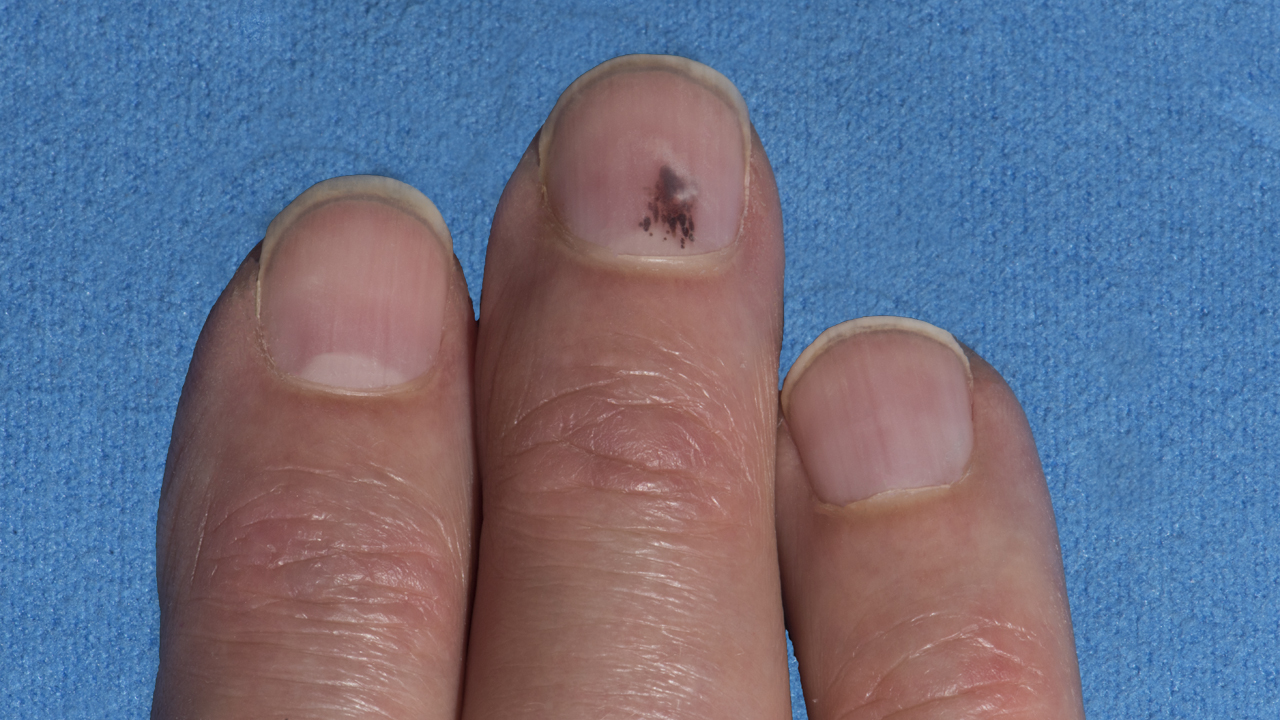
A. Asymmetrical in shape. One half of the mole doesn’t match or is
different from the other half.
B. Border is irregular. In general, your moles should be oval or
round. Contact your doctor if the mole’s border or edges become
blurred or jagged.
C. Change in the mole’s color or uneven coloring.
D. Diameter. If the size of mole is 1/8 of an inch or greater.
Other warning signs provided by the American Cancer Society:
• A mole which looks different from other moles on your body
• The moles’ surface changes (may rise, increase in size, etc.)
• Mole may begin to itch, become tender or bleed
• A sore which may not heal
• Mole expands in size
Contact your doctor or health care professional immediately if you notice a change in any of your moles. Your doctor may order a biopsy of the skin or removal of the mole if she feels it may be a serious medical issue.
The key to conquering melanoma is early detection.
Sources:
http://www.cancer.org/Cancer/SkinCancer-Melanoma/OverviewGuide/melanoma-skin-cancer-overview-risk-factors
http://www.cancer.org/Cancer/SkinCancer-Melanoma/OverviewGuide/melanoma-skin-cancer-overview-diagnosed
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000850.htm
http://health.nytimes.com/health/guides/disease/melanoma/overview.html
http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/wyntk/skin/page8
http://www.cancer.org/Cancer/SkinCancer-Melanoma/OverviewGuide/index
http://www.cancersymptoms.org/symptoms-of-melanoma-cancer
http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/documents/document/acspc-024621.pdf
Reviewed on May 30, 2011
Edited by Alison Stanton



Add a CommentComments
There are no comments yet. Be the first one and get the conversation started!