Gestational Diabetes
A New Mom's Ordeals
She walked slowly through the hallway. Her face did not show the radiance a new mother should have. Somehow it seemed dull and lifeless. She looked like someone had snatched her joy of becoming a mother right from underneath her. I could understand her pain since I was in the same situation twenty years ago. I was diagnosed with gestational diabetes during my third pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes(G.D.), by definition, is a condition in which non-diabetic women show high levels of glucose in their blood during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes could also affect women who were pre-diabetic or had diabetes mellitus before but were unaware of it. Most of the time the only way this condition is recognized is through screening for diabetes during pregnancy. Hormones produced during the pregnancy increase resistance in the pregnant woman's body to insulin causing impairment in 'glucose tolerance' thus increasing blood sugar levels.
Women with G.D. have a high risk of developing type 2 or type 1 diabetes at a later time in their lives. Risk factors include:
a. previous diagnosis of diabetes mellitus with impaired glucose tolerance/fasting blood sugar levels. b. family history of type 2 diabetes c. age-chances increase with increase in age when a woman becomes pregnant. d. ethnicity - women who are african - american, native americans, hispanics, pacific islanders, south asians are at increased risk of developing G.D. e. overweight or obesity f. diabetes during previous pregnancy with overweight child g. smoking h. polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Even though women with G.D. are asymptomatic, some show increased urination, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, bladder infection, yeast infection, blurred vision among others. Most of the time G.D. is diagnosed in the second trimester. Risk factors for the babies include increased size that could contribute complication at delivery time, low blood glucose levels, jaundice, obesity, type 2 diabetes in later years. Growth abnormalities and chemical imbalances, high blood cell mass, low levels of magnesium and calcium, respiratory distress syndrome are among other complications that babies might develop in later years.
Screening process for diagnosing G.D. includes: Oral glucose tolerance test where fasting and 2 hours post prandial glucose levels are checked. Two types of G.D. are present that include: Type A1- which is abnormal oral glucose tolerance test but normal fasting and two hours post prandial levels checked. Most of the time changes in diet and lifestyle is enough for this kind of G.D.
Type A2 G.D. is where abnormal oral glucose tolerance test shows up with high levels of fasting blood sugars as well as post prandial sugars. In this case insulin or other anti diabetic medications are required for treatment. Urinary glucose levels are also checked with a dipstick method to determine G.D. Methods of medical treatment could include insulin injections or oral medications such as Glyburide or Metformin etc... Usually diabetes tends to disappear in women after child birth only to return later in their years. A oral glucose test is recommended for determining the disappearance of the diabetes 2-4 months after the child birth (wikipedia) Most women who take insulin during pregnancy have fifty percent chance of developing diabetes withing next 5 years.
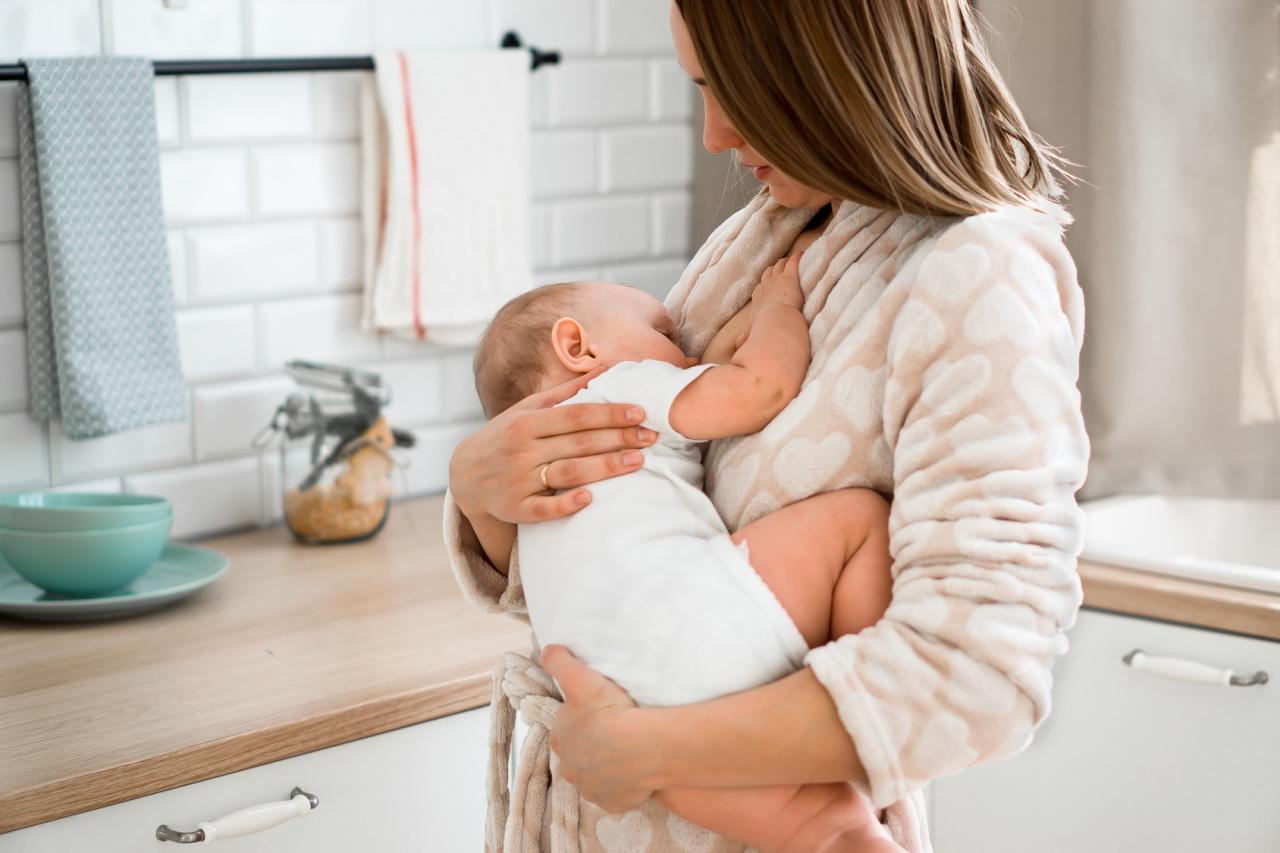
During pregnancy carbohydrate diet should be restricted to small amounts through out the day. Exercises such as walking and swimming should be made as part of maintaining blood sugars for women with G.D. Breast feeding is recommended to reduce the risk of diabetes for both mother and child post delivery. As far as my young friend is concerned, she went to see a diabetic specialist who put her on insulin and gave her instructions on how to care for herself and the baby to be born. I try my best to give her my input on G.D and give small suggestions that could help her out. With modification in diet, exercise, life style changes and proper medical care women with gestational diabetes could lead a healthy, happy pregnancy and look forward to a long and joyful parenthood. They also have the benefit of first hand experience in reducing the risks of diabetes to pass on to the off spring, because 'OUR LIFE MATTERS'





Add a CommentComments
There are no comments yet. Be the first one and get the conversation started!